Introduction:
Hemorrhagic stroke is a serious medical condition caused by bleeding in the brain. This information sheet aims to provide you with essential knowledge about hemorrhagic stroke, its risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and the importance of immediate medical attention for better outcomes. Additionally, it covers the role of surgery in the management of hemorrhagic stroke.
Understanding Hemorrhagic Stroke: The Basics
- What is Hemorrhagic Stroke?
- Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, leading to bleeding. This bleeding can cause damage to the brain tissue and impair its function.
- Types of Hemorrhagic Stroke:
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH): Bleeding occurs within the brain tissue.
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH): Bleeding occurs in the space surrounding the brain.
- Risk Factors:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Uncontrolled high blood pressure is a major risk factor for hemorrhagic stroke.
- Aneurysms: Weak spots in blood vessel walls can rupture.
- Blood-Thinning Medications: Certain medications can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Trauma: Head injuries can lead to bleeding in the brain.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms: Act FAST
- Severe Headache:
- A sudden, severe headache is a common symptom of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
- Feeling nauseous and vomiting may occur.
- Neurological Symptoms:
- Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Vision changes or loss.
- Time to Call Emergency Services:
- If you or someone you’re with experiences these symptoms, call emergency services immediately. Time is critical in stroke treatment.
Diagnosis: Confirming Hemorrhagic Stroke
- Emergency Assessment:
- Healthcare providers will conduct tests upon arrival at the hospital to assess symptoms and gather information about the onset of the stroke.
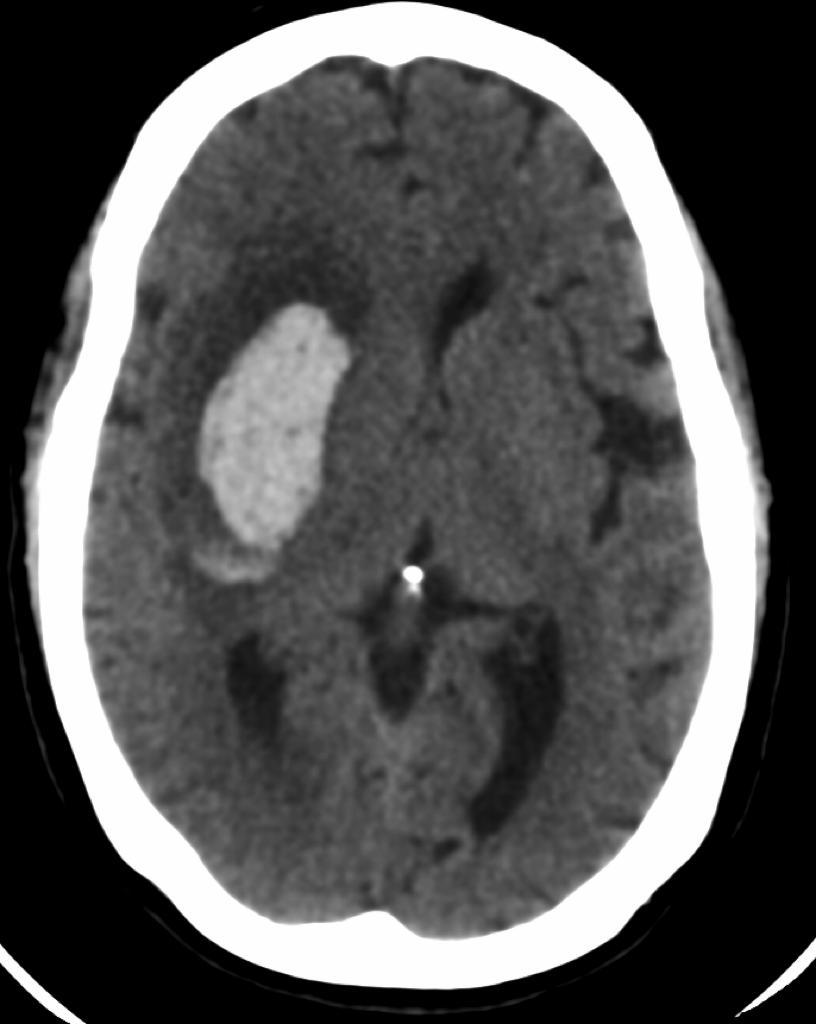
- Imaging Studies:
- CT Scan: Identifies bleeding in the brain and helps determine the type and location of the hemorrhage.
- Cerebral Angiography:
- A procedure using contrast dye to visualize blood vessels and identify abnormalities.
- Lumbar Puncture:
- Occasionally used to detect bleeding in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment: Addressing the Bleeding
- Surgical Intervention:
- Evacuation of Hematoma: In cases of significant bleeding and mass effect, surgery may be necessary to remove the accumulated blood and relieve pressure on the brain.
- Aneurysm Clipping or Coiling: If an aneurysm is identified as the cause of bleeding, surgical procedures such as clipping or coiling may be performed to prevent further rupture.
- Blood Pressure Management:
- Strict blood pressure control is crucial to prevent further bleeding.
- Rehabilitation:
- Physical and occupational therapy may be initiated to aid recovery after the acute phase.
Preventing Future Strokes: Managing Risk Factors
- Blood Pressure Control:
- Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure are essential.
- Medication Management:
- Adjustments to medications to prevent blood clotting may be necessary.
- Avoiding Risky Behaviors:
- Minimizing activities that may increase the risk of head injury.
Conclusion: Empowering You on Your Stroke Journey
Hemorrhagic stroke demands immediate medical attention. Recognizing the signs, calling for help, and receiving prompt treatment are crucial for a better outcome. Surgery may be necessary in specific cases to address bleeding and prevent further complications. Managing risk factors and adopting a proactive approach to health can significantly reduce the risk of future strokes. For personalized advice and information, consult your healthcare professional.

Wow, awesome weblog format! How lengthy have you been running a blog for?
you made blogging glance easy. The overall look of your
web site is excellent, as well as the content material!
You can see similar: sklep internetowy
and here sklep internetowy